- About Us
- Mission and Values
- Benefits
- Our Methodology
- Alliances
Our Methodology
Microsoft Solution Framework
The MSF (Microsoft Solution Framework) provides a mechanical iteration, where each one of them has a full cycle of project, and each iteration "attacks" a specific scope that we recognize as the sub domain of the problem.
Typically, each sub domain is consistent and complete in itself. Although, according to the dimensions of the problem, in some cases may choose partitions of a candidate over a subdomain into smaller units. The quantities sub domains to attack within a given project determines the number of iterations. It is possible that a project involves a single iteration.
The framework also provides guidelines on the activities within each phase. These guidelines must be understood with a non-restrictive view but as a guide to processes, adaptable to the characteristics of different project types and even with possible variations within the various projects of the same type.
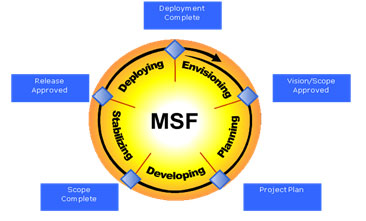
The phases of the methodology are described below, with an instantiation for Business Intelligence projects, resulting in specific products and particular aspects of the project organization.
Phases of the MSF.
Envisioning
This phase aims to establish, agree and communicate the reasons underpinning the project and its stakeholders.
To achieve this, should take over from the stakeholders, document the formal results of this survey, to establish motivations, assumptions, constraints, environment conditions both technical and human resources, and business.
It is essential to understand business analyst’s expectations, indicating past experience if any.
Planning
This phase ends with the approval of a project plan. The plan defines the strategy used to complete the project, and activities to be carried out, along with its responsible and duration commitment.
At this stage are precisely defined, the different sub domains of interest to the business. These must be prioritized for further processing at the project, as different iterations of the methodological framework.
This phase is particularly important as it establishes a baseline in the planning. Therefore, it is extremely important to have identified all the requirements to be added to the scope. Any requirement not incorporated or partially identified upon the approval of the plan, should be treated as a change to the project, and if necessary, evaluate the change. Once approved the baseline of the project should be updated.
During this phase a significant effort should be made in identifying project risks. These risks must be formally registered and a protocol for regular review, treatment and update, must be established.
Development
During this phase the solution is designed and implemented, also are done the development and configuration activities of all the software artifacts.
This includes defining the architectural model based on metrics, dimensions, hierarchies and attributes, and the integration with physical and logical model.
Also are constructed the rules for updating and implementing processes that physical instrument relations between different entities and attributes of the model with the data warehouse to the source.
The data enrichment processes are built to facilitate and improve aspects of performance of the solution.
The reports inquired to business users are built, interacting with those users on regular basis for assessment of correctness, interoperability and usability.
As part of the iteration in the used methodology changes to documents generated in previous stages also appear.
Stabilization
In this instance, the tests are and adjustments are made to reach a publishable version of the solution.
All software components, from the data source to the visible values at operating level are tested in an integrated manner.
At this stage there is great participation by the business users again. It is important to have reports generated as reference that can be used to establish the users acceptance criteria and test the whole process.
Just as happens during development, at this stage errors may occur involving the review of the documents generated in previous stages.
Deployment
During this phase the activities necessary to implement the solution are carried out.
This may involve data migration, special data loading for the sole purpose of migration, configuration and access permissions in the productive environment, and any support activities that put the solution in operation.
Also are contemplated within this phase activities related to the management of organizational change. This includes training for users and administrators on the tools selected.
It is possible that new internal procedures may need to be generated and put into operation.

